Understanding Demodex Blepharitis: A Comprehensive Review
Demodex blepharitis is a prevalent and often underdiagnosed condition caused by an infestation of Demodex mites.This condition leads to inflammation of the eyelids and can significantly impact the quality of life.
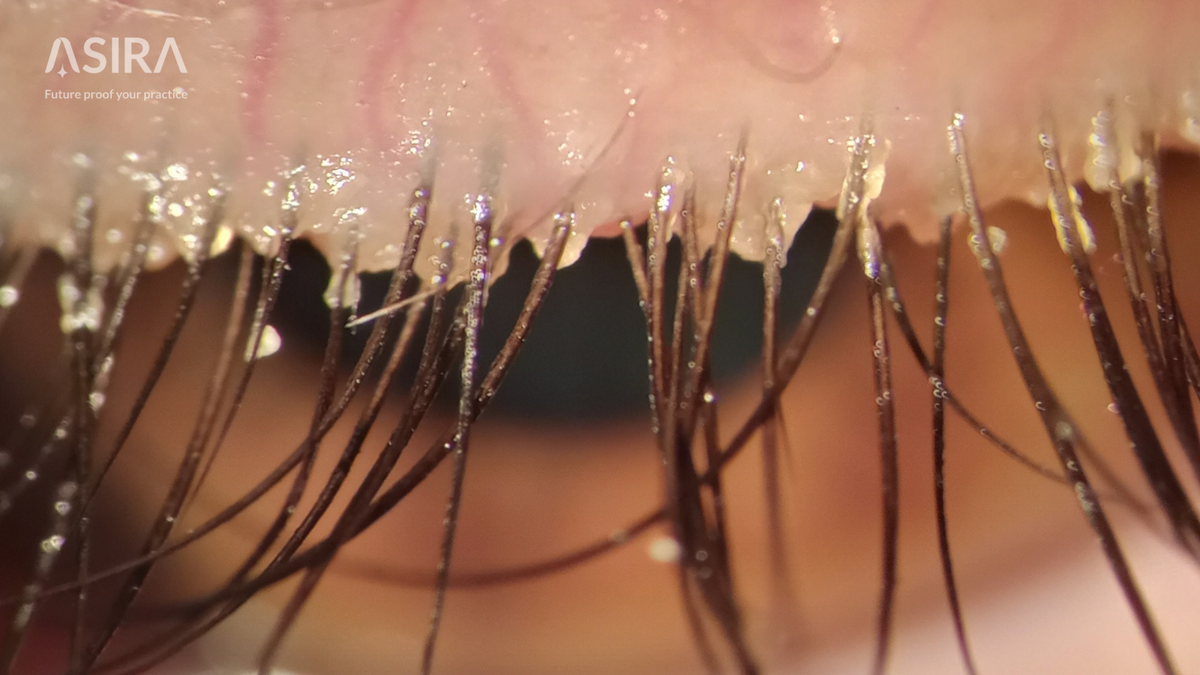
Demodex blepharitis is a prevalent and often underdiagnosed condition caused by an infestation of Demodex mites, primarily Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis. This condition leads to inflammation of the eyelids and can significantly impact the quality of life. The recent study by Martínez-Pulgarín et al. (2021) provides a systematic review and meta-analysis of various interventions for Demodex blepharitis, evaluating their effectiveness and safety.
Introduction to Demodex Blepharitis
Blepharitis involves inflammation of the eyelids, often associated with meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD), which contributes to symptoms such as burning, itching, tearing, and redness. Demodex mites are a significant etiological factor in blepharitis, with a high prevalence in the elderly population. The study highlights that up to 100% of individuals over 70 years may harbour these mites.
The pathogenesis of Demodex blepharitis includes direct damage through micro-abrasions and gland blockage, acting as vectors for bacteria like Staphylococci, and inducing immune responses through hypersensitivity to mite debris.
Economic Impact
The economic burden of blepharitis, particularly in dry eye disease (DED) cases, is substantial. In the U.S., the annual treatment cost for DED is approximately $3.84 billion, with significant costs reported in Europe and Asia as well. The costs extrapolated for Demodex blepharitis are similarly high, though specific data for Latin America and Colombia are lacking.
Diagnostic Methods
Accurate diagnosis of Demodex blepharitis relies on clinical evaluation, with signs such as cylindrical dandruff at the base of the lashes being pathognomonic. Confirmation is achieved through microscopic visualization of mites from epilated lashes or in vivo confocal microscopy.
Interventions Evaluated
The meta-analysis included 18 studies encompassing 1195 participants and 1574 eyes, examining 29 different interventions. The primary outcomes assessed were mite counts per eyelash, total eradication rates, and secondary outcomes such as Tear Break-Up Time (TBUT), Ocular Surface Disease Index (OSDI), and adverse reactions.
Key Findings
Demodex Count Reduction:
- Overall, the interventions showed a significant reduction in Demodex counts with a mean difference of -2.07 mites per eyelash.
- Systemic and topical ivermectin-metronidazole combinations were the most effective, with reductions up to -7.50 mites per eyelash.
- Tea tree oil (TTO) and its derivatives, such as terpinen-4-ol, also demonstrated significant mite count reductions.
Total Eradication of Mites:
- The pooled risk ratio (RR) for total eradication favored intervention groups with an RR of 1.84.
- Effective interventions included TTO lid scrubs, manuka honey, and ivermectin-metronidazole combinations.
Adverse Reactions:
- Adverse reactions were more common in TTO-derived treatments, though all were mild, including discomfort and transient irritation.
- The risk difference for adverse reactions was 0.24, indicating a higher likelihood of mild adverse effects in the intervention groups.
Treatment Considerations
Pharmacological treatments, particularly systemic and topical ivermectin-metronidazole, were superior to non-pharmacological interventions (mechanical, thermal, and pulsed light) in reducing mite counts and achieving total eradication. However, TTO and its derivatives, despite their effectiveness, were associated with higher adverse reaction rates.
The study underscores the need for long-term follow-up to determine reinfestation rates and the overall sustainability of treatment effects.
Alternative Therapies
Alternative treatments evaluated included:
- Intense Pulsed Light (IPL): Showed improvements in TBUT and OSDI, though not significantly affecting mite counts.
- 1,2-Octanediol: Demonstrated efficacy in mite reduction by disrupting the parasite’s lipid cover.
- Manuka Honey: Exhibited antibacterial and anti-demodectic properties with significant eradication rates.
Study Strengths and Limitations
This systematic review and meta-analysis offer comprehensive insights into the effectiveness of various treatments for Demodex blepharitis. However, limitations include heterogeneity among studies, lack of standardization, and short follow-up periods. The absence of data on reinfestation rates post-treatment is a critical gap that future research needs to address.
Conclusion
The study by Martínez-Pulgarín et al. (2021) highlights the effectiveness of pharmacological interventions, particularly ivermectin-metronidazole, in treating Demodex blepharitis. TTO and its derivatives, despite their popularity, come with higher rates of mild adverse reactions. The findings advocate for more standardized, long-term studies to better understand treatment sustainability and reinfestation rates.
For clinicians and researchers, this meta-analysis provides valuable guidance on selecting effective treatments and underscores the importance of balancing efficacy with safety in managing Demodex blepharitis.
References:
- Martínez-Pulgarín DF, Ávila MY, Rodríguez-Morales AJ. Interventions for Demodex blepharitis and their effectiveness: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Contact Lens Anterior Eye. 2021;44:101453. Available at Elsevier.
ASIRA is a simple and secure, cloud-based software tool, built BY optometrists FOR optometrists, that helps eye care professionals reduce the time and effort required to maintain clinical records, schedule appointments, generate bills, manage inventory and much more!
To find out more, visit www.asira.health and sign up for a 30-Day FREE TRIAL! If you're a new practice owner or a fresh graduate thinking of entrepreneurship, visit www.asira.health/optompreneur to learn how ASIRA can help reduce your costs and increase revenue.





Comments ()